算法
数据里有{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},请随机打乱顺序,生成一个新的数组(请以代码实现)
public class Demo1 {
public static int[] srand(int[] a) {
int[] b = new int[a.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
int tmp = (int) (Math.random() * (a.length - 1));
b[i] = a[tmp];
int change = a[a.length - 1 - i];
a[a.length - 1 - i] = a[tmp];
a[tmp] = change;
}
return b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(srand(a)));
}
}
写出代码判断一个整数是不是 2 的阶次方(请代码实现,谢绝调用 API 方法)
class Demo2 {
public static boolean check(int sum) {
boolean flag = true; //判断标志
while (sum > 1) {
if (sum % 2 == 0) {
sum = sum / 2;
} else {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int sum = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(sum + " 是不是2的阶次方:" + check(sum));
}
}
假设今日是 2015 年 3 月 1 日,星期日,请算出 13 个月零 6 天后是星期几,距离现在多少天(请用代码实现,谢绝调用 API 方法)
class Demo3 {
public static String[] week = {"星期日", "星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六"};
public static int i = 0;
public static int[] monthday1 = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
public static int[] monthday2 = {0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
//查看距离当前天数的差值
public static String distance(int year, int month, int day, int newMonth, int newDay) {
int sum = 0; //设定初始距离天数
if (month + newMonth >= 12) {
if (((year + 1) % 4 == 0 && (year + 1) % 100 != 0) || (year + 1) % 400 == 0) {
sum += 366 + newDay;
for (int i = 0; i < newMonth - 12; i++) {
sum += monthday1[month + i];
}
} else {
sum += 365 + newDay;
for (int i = 0; i < newMonth - 12; i++) {
sum += monthday1[month + i];
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < newMonth; i++) {
sum += monthday1[month + i];
}
sum += newDay;
}
return week[sum % 7];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入当前年份");
int year = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入当前月份");
int month = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入当前天数");
int day = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入当前是星期几:以数字表示,如:星期天 为 0");
int index = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("今天是:" + year + "-" + month + "-" + day + " " + week[index]);
System.err.println("请输入相隔月份");
int newMonth = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入剩余天数");
int newDay = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("经过" + newMonth + "月" + newDay + "天后,是" + distance(year, month, day, newMonth, newDay));
}
}
有两个篮子,分别为 A 和 B,篮子 A 里装有鸡蛋,篮子 B 里装有苹果,请用面向对象的思想实现两个篮子里的物品交 换(请用代码实现)
package top.wyix.java.sf;
/**
* 面向对象思想实现篮子物品交换
*
* @author wyix
*/
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建篮子
Basket A = new Basket("A");
Basket B = new Basket("B");
//装载物品
A.load("鸡蛋");
B.load("苹果");
//交换物品
A.change(B);
A.show();
B.show();
}
}
class Basket {
public String name; //篮子名称
private Goods goods; //篮子中所装物品
public Basket(String name) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.name = name;
System.out.println(name + "篮子被创建");
}
public void load(String name) {
goods = new Goods(name);
System.out.println(this.name + "装载了" + name + "物品");
}
public void change(Basket B) {
System.out.println(this.name + " 和 " + B.name + "中的物品发生了交换");
String tmp = this.goods.getName();
this.goods.setName(B.goods.getName());
B.goods.setName(tmp);
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(this.name + "中有" + goods.getName() + "物品");
}
}
class Goods {
public String name;
public Goods(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
二分查找
又叫折半查找,要求待查找的序列有序。每次取中间位置的值与待查关键字比较,如果中间位置的值比待查关键字大,则在前半部分循环这个查找的过程,如果中间位置的值比 待查关键字小,则在后半部分循环这个查找的过程。直到查找到了为止,否则序列中没有待查的关键字。
public class Demo6 {
public static int biSearch(int[] array, int a) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = array.length - 1;
int mid;
while (lo <= hi) {
mid = (lo + hi) / 2;//中间位置
if (array[mid] == a) {
return mid + 1;
} else if (array[mid] < a) { //向右查找 lo=mid+1;
} else { //向左查找
hi = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
冒泡排序算法
- 1)比较前后相邻的二个数据,如果前面数据大于后面的数据,就将这二个数据交换。
- (2)这样对数组的第 0 个数据到 N-1 个数据进行一次遍历后,最大的一个数据就“沉” 到数组第 N-1 个位置。
- (3) N=N-1,如果 N 不为 0 就重复前面二步,否则排序完成。
public static void bubbleSort1(int[] a, int n) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {//表示 n 次排序过程。
for (j = 1; j < n - i; j++) {
if (a[j - 1] > a[j]) {//前面的数字大于后面的数字就交换 //交换 a[j-1]和 a[j]
int temp;
temp = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
插入排序算法
通过构建有序序列,对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应的位置并插入。插入排序非常类似于整扑克牌。在开始摸牌时,左手是空的,牌面朝下放在桌 上。接着, 一次从桌上摸起一张牌,并将它插入到左手一把牌中的正确位置上。 为了找到这张牌的正确位置,要将它与手中已有的牌从右到左地进行比较。无论什么时候,左手 中的牌都是排好序的。如果输入数组已经是排好序的话,插入排序出现最佳情况,其运行时间是输入规模的一个线性函数。如果输入数组是逆序排列的,将出现最坏情况。平均 情况与最坏情况一样,其时间代价是(n2)。

public void sort(int arr[]) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
//插入的数
int insertVal = arr[i];
//被插入的位置(准备和前一个数比较)
int index = i - 1;
//如果插入的数比被插入的数小
while (index >= 0 && insertVal < arr[index]) {
//将把 arr[index] 向后移动
arr[index + 1] = arr[index]; //让 index 向前移动
index--;
}
//把插入的数放入合适位置
arr[index + 1] = insertVal;
}
}
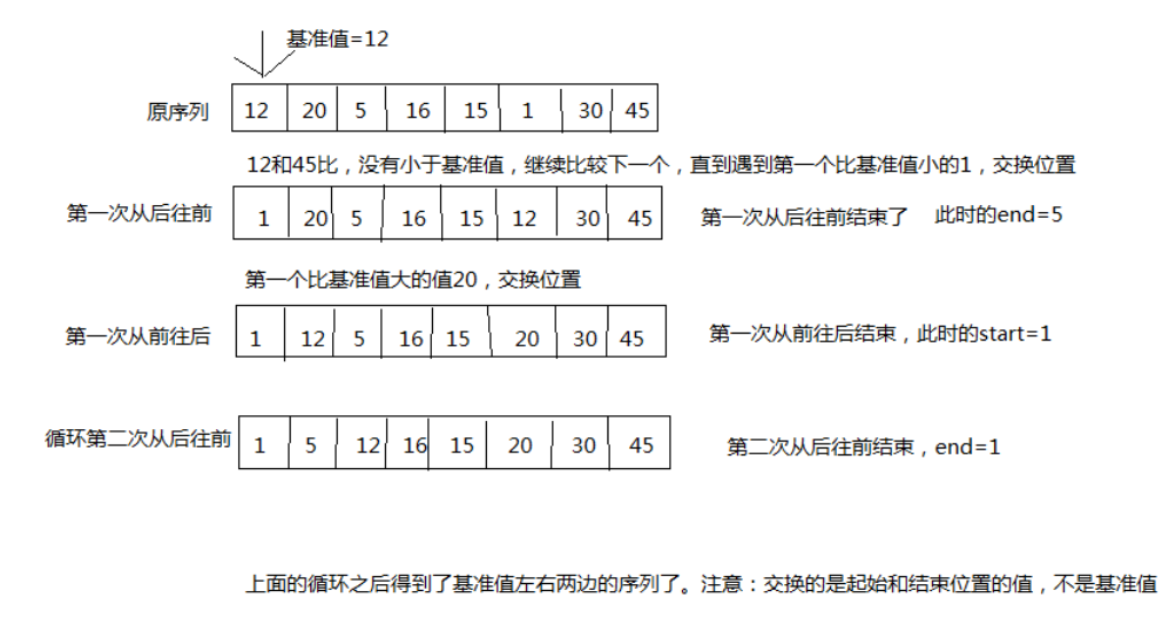
快速排序算法
快速排序的原理:选择一个关键值作为基准值。比基准值小的都在左边序列(一般是无序的),比基准值大的都在右边(一般是无序的)。 一般选择序列的第一个元素。
一次循环: 从后往前比较,用基准值和最后一个值比较,如果比基准值小的交换位置,如果没有继续比较下一个,直到找到第一个比基准值小的值才交换。 找到这个值之后,又 从前往后开始比较,如果有比基准值大的,交换位置,如果没有继续比较下一个,直到找到第一个比基准值大的值才交换。直到从前往后的比较索引>从后往前比较的索引,结束 第一次循环,此时,对于基准值来说,左右两边就是有序的了。
public void sort(int[] a, int low, int high) {
int start = low;
int end = high;
int key = a[low];
while (end > start) {
//从后往前比较
while (end > start && a[end] >= key)
//如果没有比关键值小的,比较下一个,直到有比关键值小的交换位置,然后又从前往后比较
end--;
if (a[end] <= key) {
int temp = a[end];
a[end] = a[start];
a[start] = temp;
}
//从前往后比较
while (end > start && a[start] <= key) {
//如果没有比关键值大的,比较下一个,直到有比关键值大的交换位置
start++;
if (a[start] >= key) {
int temp = a[start];
a[start] = a[end];
a[end] = temp;
}
//此时第一次循环比较结束,关键值的位置已经确定了。左边的值都比关键值小,右边的值都比关键值大,但是两边的顺序还有可能是不一样的,进行下面的递归调用
}
//递归
if (start > low)
sort(a, low, start - 1);//左边序列。第一个索引位置到关键值索引-1
if (end < high) sort(a, end + 1, high);//右边序列。从关键值索引+1 到最后一个
}
}
希尔排序算法
基本思想:先将整个待排序的记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序,待整个序列中的记录“基本有序” 时,再对全体记录进行依次直接插入排序。
- 操作方法:选择一个增量序列 t1, t2, …, tk,其中 ti>tj, tk=1;
- 按增量序列个数 k,对序列进行 k 趟排序;
- 每趟排序,根据对应的增量 ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为 m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排序。仅增量因子为 1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为 整个序列的长度。
private void shellSort(int[] a) {
int dk = a.length / 2;
while (dk >= 1) {
ShellInsertSort(a, dk);
dk = dk / 2;
}
}
private void ShellInsertSort(int[] a, int dk) {
//类似插入排序,只是插入排序增量是 1,这里增量是 dk,把 1 换成 dk 就可以了
for (int i = dk; i < a.length; i++) {
if (a[i] < a[i - dk]) {
int j;
int x = a[i];//x 为待插入元素
a[i] = a[i - dk];
for (j = i - dk; j >= 0 && x < a[j]; j = j - dk) {
//通过循环,逐个后移一位找到要插入的位置。
a[j + dk] = a[j];
}
a[j + dk] = x;//插入 }
}
}
}
归并排序算法
归并(Merge)排序法是将两个(或两个以上)有序表合并成一个新的有序表,即把待排序序列分为若干个子序列,每个子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并为整体有序 序列。 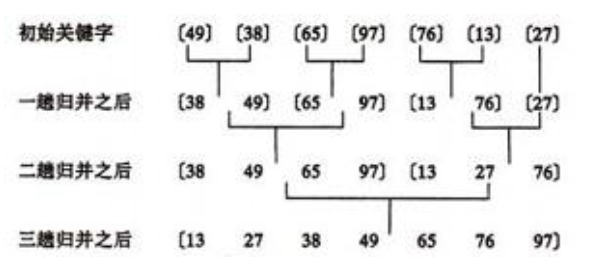
package top.wyix.java.sf;
/**
* @author wyix
*/
public class MergeSortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = new int[]{5, 3, 6, 2, 1, 9, 4, 8, 7};
print(data);
mergeSort(data);
System.out.println("排序后的数组: ");
print(data);
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] data) {
sort(data, 0, data.length - 1);
}
public static void sort(int[] data, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right)
return;
// 找出中间索引
int center = (left + right) / 2;
// 对左边数组进行递归
sort(data, left, center);
// 对右边数组进行递归
sort(data, center + 1, right);
// 合并
merge(data, left, center, right);
print(data);
}
/**
* 将两个数组进行归并,归并前面 2 个数组已有序,归并后依然有序
*
* @param data 数组对象
* @param left 左数组的第一个元素的索引
* @param center 左数组的最后一个元素的索引, center+1 是右数组第一个元素的索引
* @param right 右数组最后一个元素的索引
*/
public static void merge(int[] data, int left, int center, int right) {
// 临时数组
int[] tmpArr = new int[data.length]; // 右数组第一个元素索引
int mid = center + 1;
// third 记录临时数组的索引
int third = left;
// 缓存左数组第一个元素的索引
int tmp = left;
while (left <= center && mid <= right) {
// 从两个数组中取出最小的放入临时数组
if (data[left] <= data[mid]) {
tmpArr[third++] = data[left++];
} else {
tmpArr[third++] = data[mid++];
}
}
// 剩余部分依次放入临时数组(实际上两个 while 只会执行其中一个)
while (mid <= right) {
tmpArr[third++] = data[mid++];
}
while (left <= center) {
tmpArr[third++] = data[left++];
}
// 将临时数组中的内容拷贝回原数组中
// (原 left-right 范围的内容被复制回原数组)
while (tmp <= right) {
data[tmp] = tmpArr[tmp++];
}
}
public static void print(int[] data) {
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
桶排序算法
桶排序的基本思想是: 把数组 arr 划分为 n 个大小相同子区间(桶),每个子区间各自排序,最后合并 。计数排序是桶排序的一种特殊情况,可以把计数排序当成每个桶里只有 一个元素的情况。
- 1.找出待排序数组中的最大值 max、最小值 min
- 2.我们使用 动态数组 ArrayList 作为桶,桶里放的元素也用 ArrayList 存储。桶的数量为(maxmin)/arr.length+1
- 3.遍历数组 arr,计算每个元素 arr[i] 放的桶
- 4.每个桶各自排序
public static void bucketSort(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
min = Math.min(min, arr[i]);
}
//创建桶
int bucketNum = (max - min) / arr.length + 1;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketArr = new ArrayList<>(bucketNum);
for (int i = 0; i < bucketNum; i++) {
bucketArr.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
//将每个元素放入桶
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int num = (arr[i] - min) / (arr.length);
bucketArr.get(num).add(arr[i]);
}
//对每个桶进行排序
for (int i = 0; i < bucketArr.size(); i++) {
Collections.sort(bucketArr.get(i));
}
}
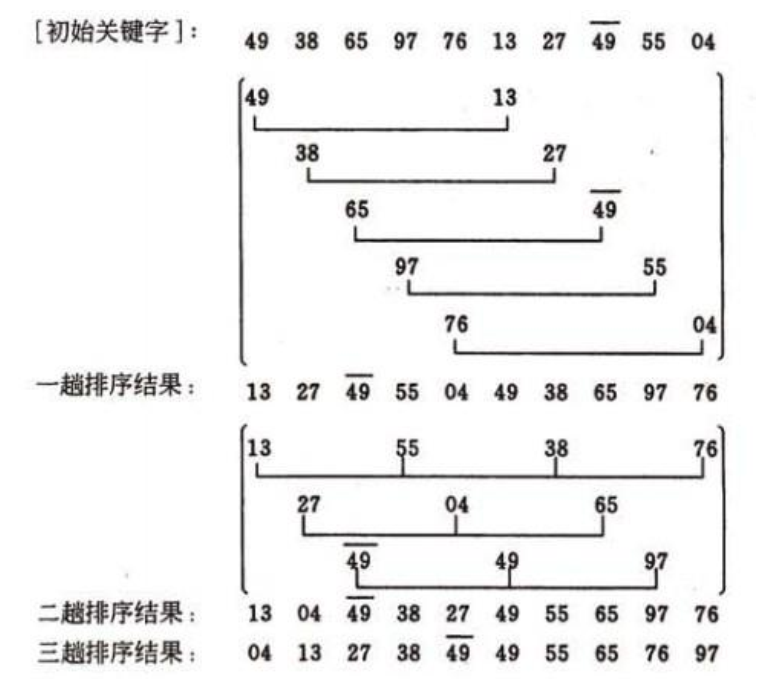
基数排序算法
将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度,数位较短的数前面补零。然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后,数列就 变成一个有序序列。
public class radixSort {
int a[] = {49, 38, 65, 97, 76, 13, 27, 49, 78, 34, 12, 64, 5, 4, 62, 99, 98, 54, 101, 56, 17, 18, 23, 34, 15, 35, 2 5, 53, 51};
public radixSort() {
sort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
public void sort(int[] array) {
//首先确定排序的趟数;
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] > max) {
max = array[i];
}
}
int time = 0;
//判断位数;
while (max > 0) {
max /= 10;
time++;
}
//建立 10 个队列;
List<ArrayList> queue = new ArrayList<ArrayList>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> queue1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
queue.add(queue1);
}
//进行 time 次分配和收集;
for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) {
//分配数组元素;
for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
//得到数字的第 time+1 位数;
int x = array[j] % (int) Math.pow(10, i + 1) / (int) Math.pow(10, i);
ArrayList<Integer> queue2 = queue.get(x);
queue2.add(array[j]);
queue.set(x, queue2);
}
int count = 0;//元素计数器;
//收集队列元素;
for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
while (queue.get(k).size() > 0) {
ArrayList<Integer> queue3 = queue.get(k);
array[count] = queue3.get(0);
queue3.remove(0);
count++;
}
}
}
}
}
剪枝算法
在搜索算法中优化中,剪枝,就是通过某种判断,避免一些不必要的遍历过程,形象的说,就是剪去了搜索树中的某些“枝条”,故称剪枝。应用剪枝优化的核心问题是设计剪枝判 断方法,即确定哪些枝条应当舍弃,哪些枝条应当保留的方法。
回溯算法
回溯算法实际上一个类似枚举的搜索尝试过程,主要是在搜索尝试过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。
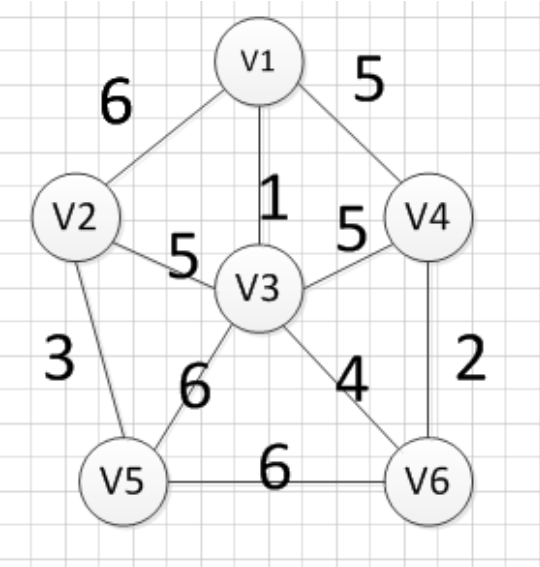
最短路径算法
从某顶点出发,沿图的边到达另一顶点所经过的路径中,各边上权值之和最小的一条路径叫做最短路径。解决最短路的问题有以下算法, Dijkstra 算法, Bellman-Ford 算法, Floyd 算法和 SPFA 算法等
最小生成树算法
现在假设有一个很实际的问题:我们要在 n 个城市中建立一个通信网络,则连通这 n 个城市需要布置 n-1 一条通信线路,这个时候我们需要考虑如何在成本最低的情况下建立这 个通信网?
于是我们就可以引入连通图来解决我们遇到的问题, n 个城市就是图上的 n 个顶点,然后,边表示两个城市的通信线路,每条边上的权重就是我们搭建这条线路所需要的成本, 所以现在我们有 n 个顶点的连通网可以建立不同的生成树,每一颗生成树都可以作为一个通信网,当我们构造这个连通网所花的成本最小时,搭建该连通网的生成树,就称为最 小生成树。
构造最小生成树有很多算法,但是他们都是利用了最小生成树的同一种性质: MST 性质(假设 N=(V,{E})是一个连通网, U 是顶点集 V 的一个非空子集,如果(u, v)是一条具 有最小权值的边,其中 u 属于 U, v 属于 V-U,则必定存在一颗包含边(u, v)的最小生成树),下面就介绍两种使用 MST 性质生成最小生成树的算法:普里姆算法和克鲁斯 卡尔算法。
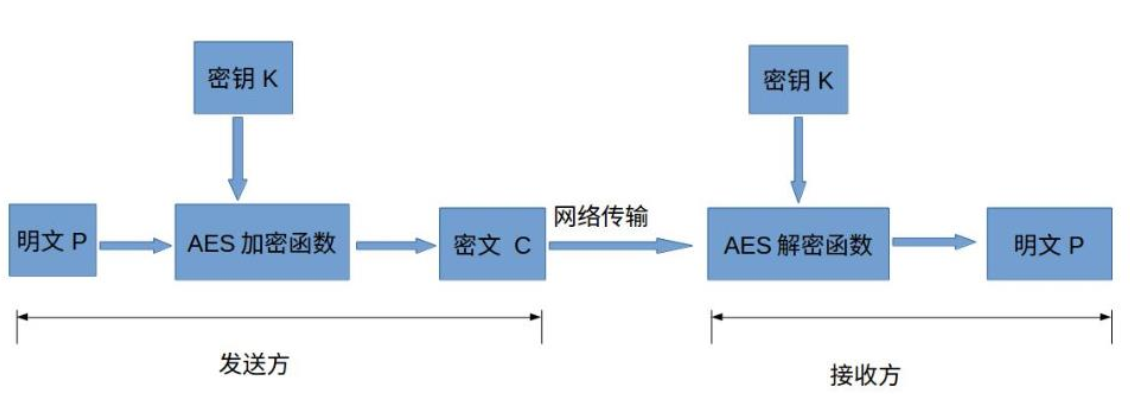
AES
高级加密标准(AES,Advanced Encryption Standard)为最常见的对称加密算法(微信小程序加密传输就是用这个加密算法的)。对称加密算法也就是加密和解密用相同的密钥,具体 的加密流程如下图:
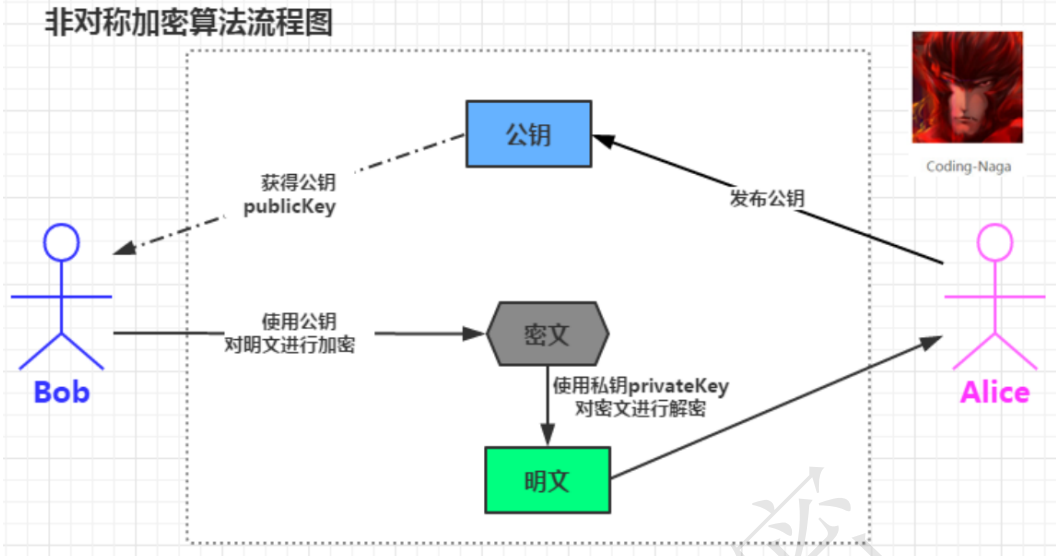
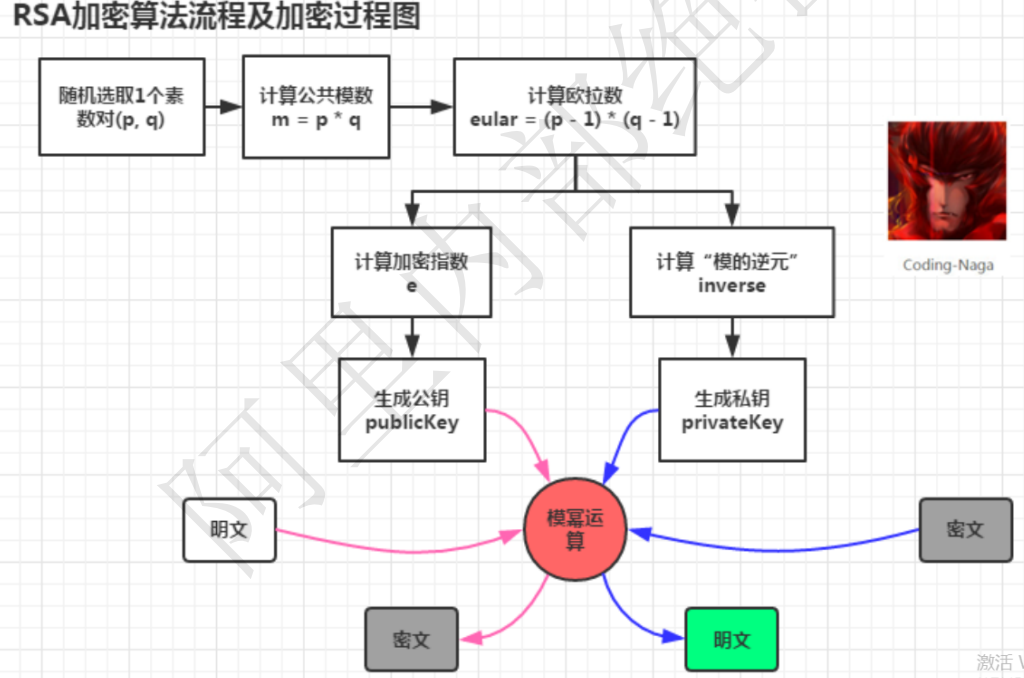
RSA
RSA 加密算法是一种典型的非对称加密算法,它基于大数的因式分解数学难题,它也是应用最广泛的非对称加密算法。 非对称加密是通过两个密钥(公钥-私钥)来实现对数据的加密和解密的。公钥用于加密,私钥用于解密。
CRC
循环冗余校验(Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC)是一种根据网络数据包或电脑文件等数据产生简短固定位数校验码的一种散列函数,主要用来检测或校验数据传输或者保存后可能 出现的错误。它是利用除法及余数的原理来作错误侦测的。
MD5
MD5 常常作为文件的签名出现,我们在下载文件的时候,常常会看到文件页面上附带一个扩展名为.MD5 的文本或者一行字符,这行字符就是就是把整个文件当作原数据通过 MD5 计算后的值,我们下载文件后,可以用检查文件 MD5 信息的软件对下载到的文件在进行一次计算。两次结果对比就可以确保下载到文件的准确性。 另一种常见用途就是网 站敏感信息加密,比如用户名密码,支付签名等等。随着 https 技术的普及,现在的网站广泛采用前台明文传输到后台, MD5 加密(使用偏移量)的方式保护敏感数据保护站点 和数据安全。
更多算法练习
更多算法练习题,请访问 https://leetcode-cn.com/problemset/algorithms/